Drug addiction, also called substance use disorder, is a disease that affects a person's brain and behavior and leads to an inability to control the use of a legal or illegal drug or medication. Substances such as alcohol, marijuana and nicotine also are considered drugs. When you're addicted, you may continue using the drug despite the harm it causes.
There are effective and FDA-approved medications to treat some substance use disorders, particularly opioid use disorders, tobacco use disorder, and alcohol use disorder. Therapy and behavioral health treatment is proven to treat substance use disorders, and is often combined with medication.
Addiction is the most pressing public health crisis of our time. It is a chronic, medical condition that can impair health and function and is characterized by repeated use of a substance despite harmful consequences. Prolonged substance use can cause changes to the brain, making it important to get someone with unhealthy alcohol or drug use into treatment as quickly as possible. People with substance use disorders often have other chronic health conditions, and they can be made more difficult to treat because of substance use. There is effective treatment available for substance use disorders and most people with substance use disorders do recover.
Addiction Can Occur From:
- Genetic predisposition
- Psychological factors (i.e., stress, depression, anxiety, eating disorders, personality and other psychiatric disorders)
- Environmental influences (i.e., exposure to physical, sexual, or emotional abuse or trauma, substance use either in the family or among peers, references within popular culture)
- Starting use of alcohol, nicotine or other drugs at an early age
More than 20 million people in the United States now live with an addiction, costing more than $400 billion in health-related costs each year. At BMC, we care for thousands of individuals with addiction each year. In fact, 34% of individuals transported by Boston EMS for drug-related illnesses are brought to BMC for care.
Who is Affected?
Everyone is affected by addiction. It is not a disease of the underserved, of those who encountered a rough patch in life, or the uneducated. It is affecting every socioeconomic bracket of our country, every neighborhood, and every ethnicity. Consider the following:
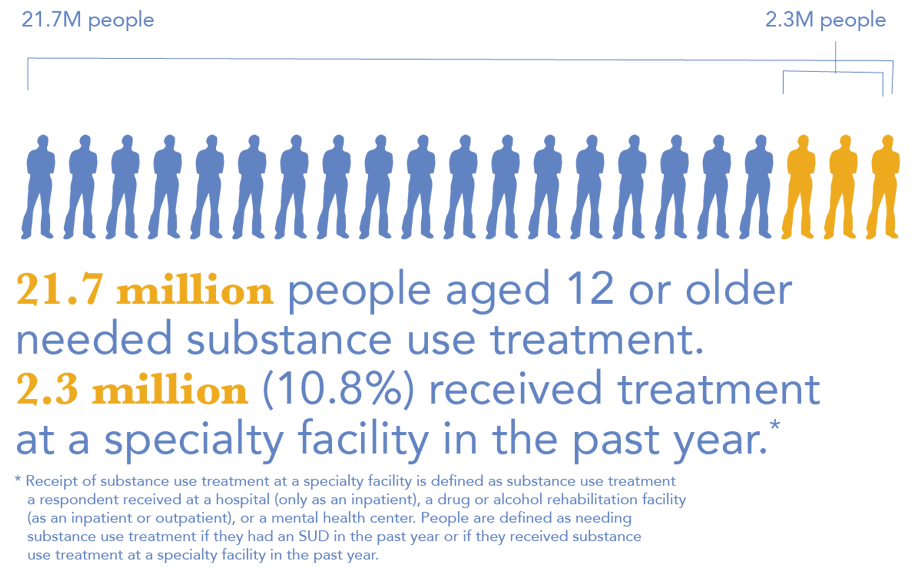
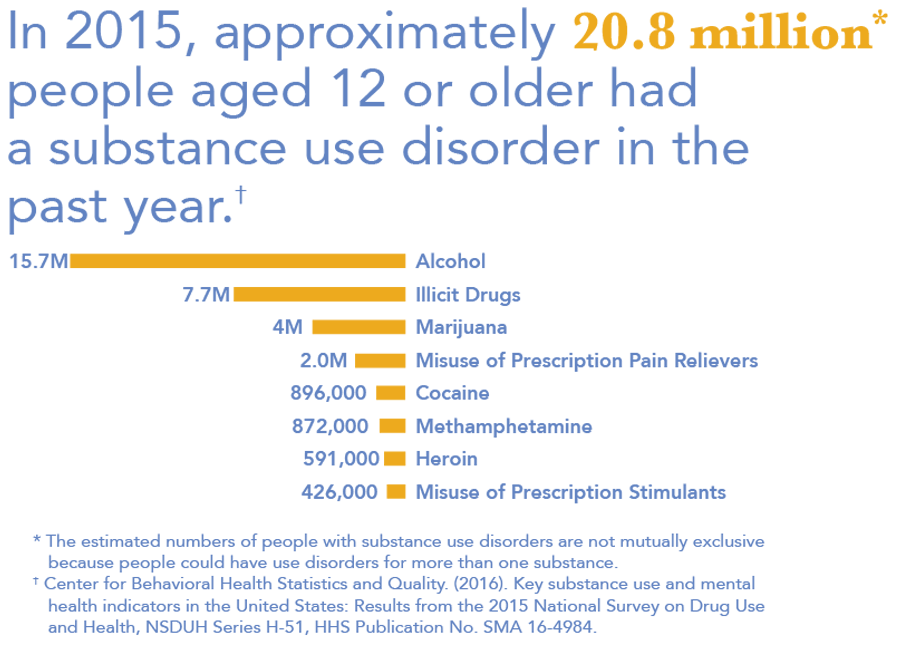



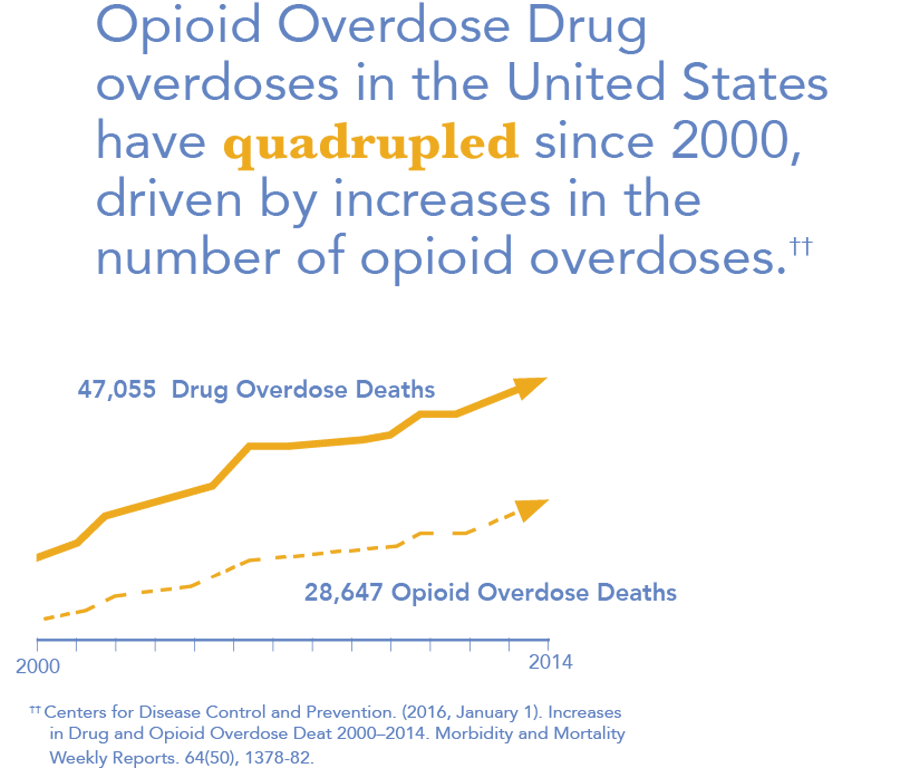
Overdose Deaths
The most dramatic metric of substance abuse – overdose deaths – is increasing rapidly, particularly in Massachusetts.
Grayken Center
Through the Grayken Center for Addiction, BMC offers comprehensive treatment programs are tailored to meet the unique needs of patients of all ages and walks of life.
To schedule an appointment with an addiction specialist, please call 617-638-5500, or click on a service to learn more.
